GPS fertiliser spreader
Description
Practice abstract
Global positioning system (GPS) has been incorporated into agricultural machinery to improve the accuracy and evenness of fertiliser spreading to optimise yield and grass quality and to protect the environment. One of the biggest savings results from switching the spreader on and off at the correct time when turning at the headland. Headland control and getting the ins and outs right is particularly important for grassland farmers. Farmers can also set the spreader to spread lower amounts particularly if clover is incorporated on farm.
Denis O Dea farms in Limerick, Ireland. The farm is a pasture-based spring calving dairy farm and they spread their own fertiliser using a GPS system. They want to improve efficiency when spreading fertiliser and reduce any waste. Denis finds the system simple to use. It is easy to calibrate and allows them to spread their desired level of fertiliser when required.
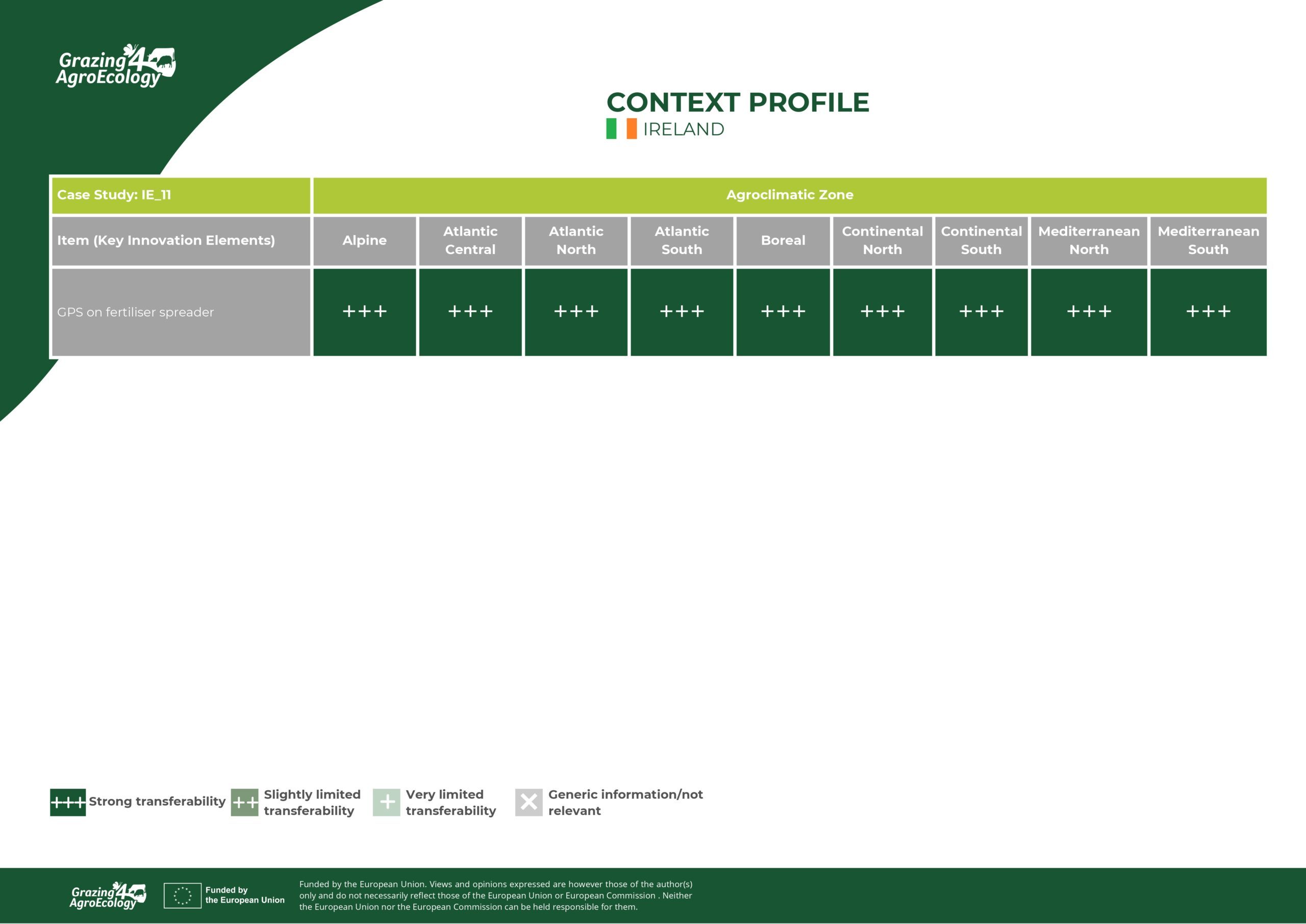
Context profil

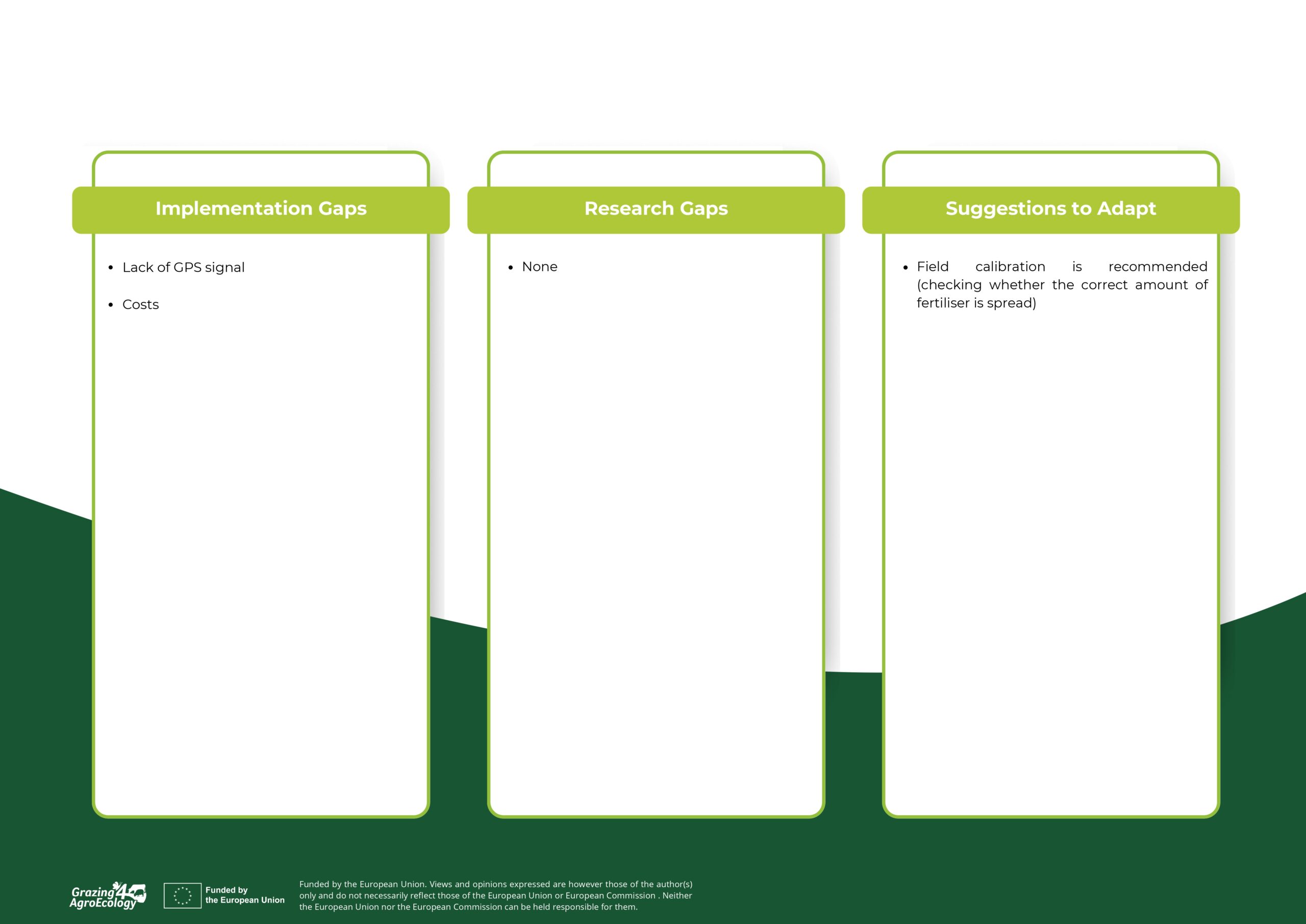
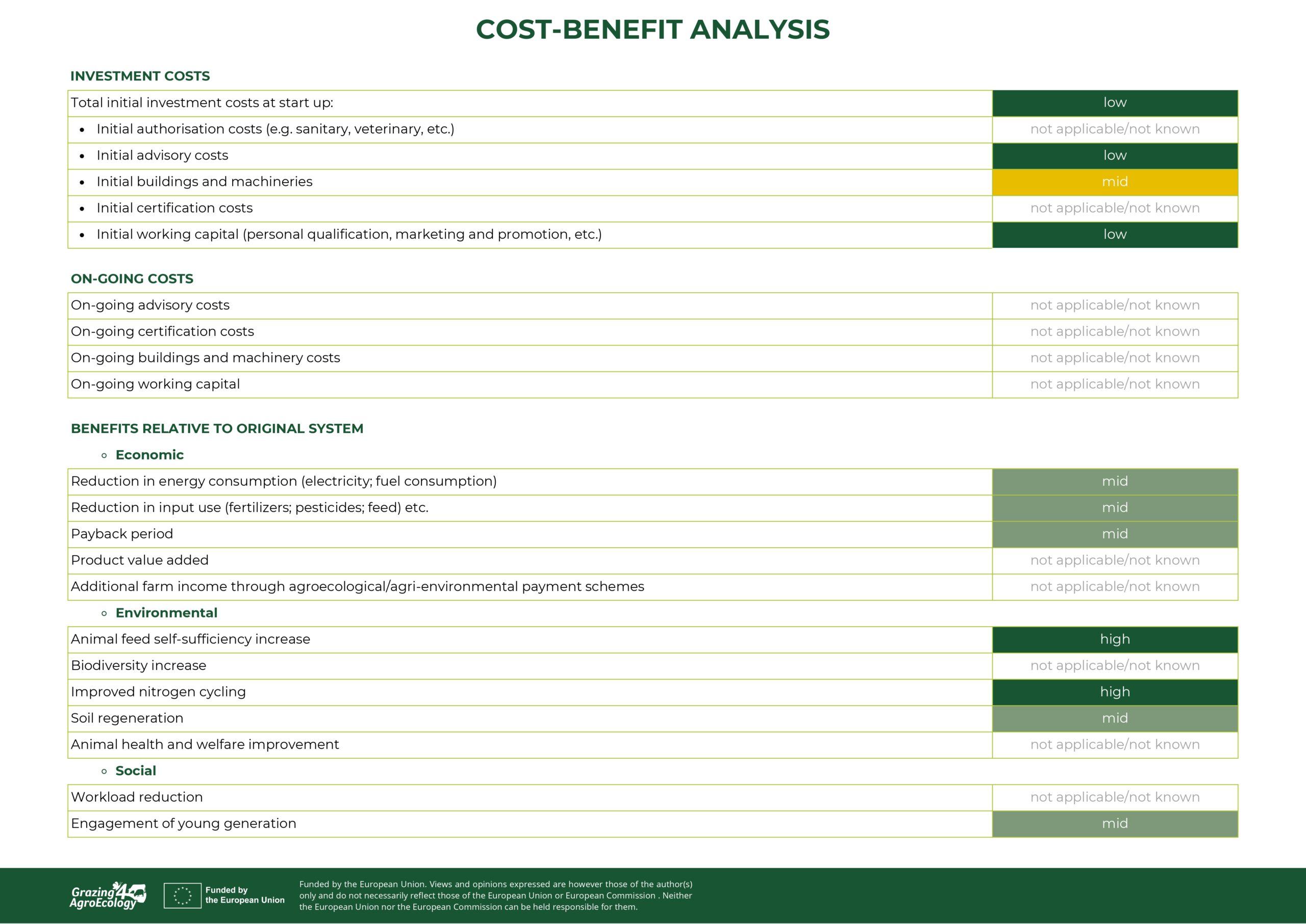

Additional information
| Main domain of innovation | Improvement of nutrient cycle |
|---|---|
| Agroclimatic area | Atlantic north |
| Climate | Moderate rainfall |
| Soil Type | Loarm |
| Management | Pasture dairy |
| Technical | Computer-based |
| Finance/investment | Low |
| Market | Local-rural |
| Social | Full-time farmer |